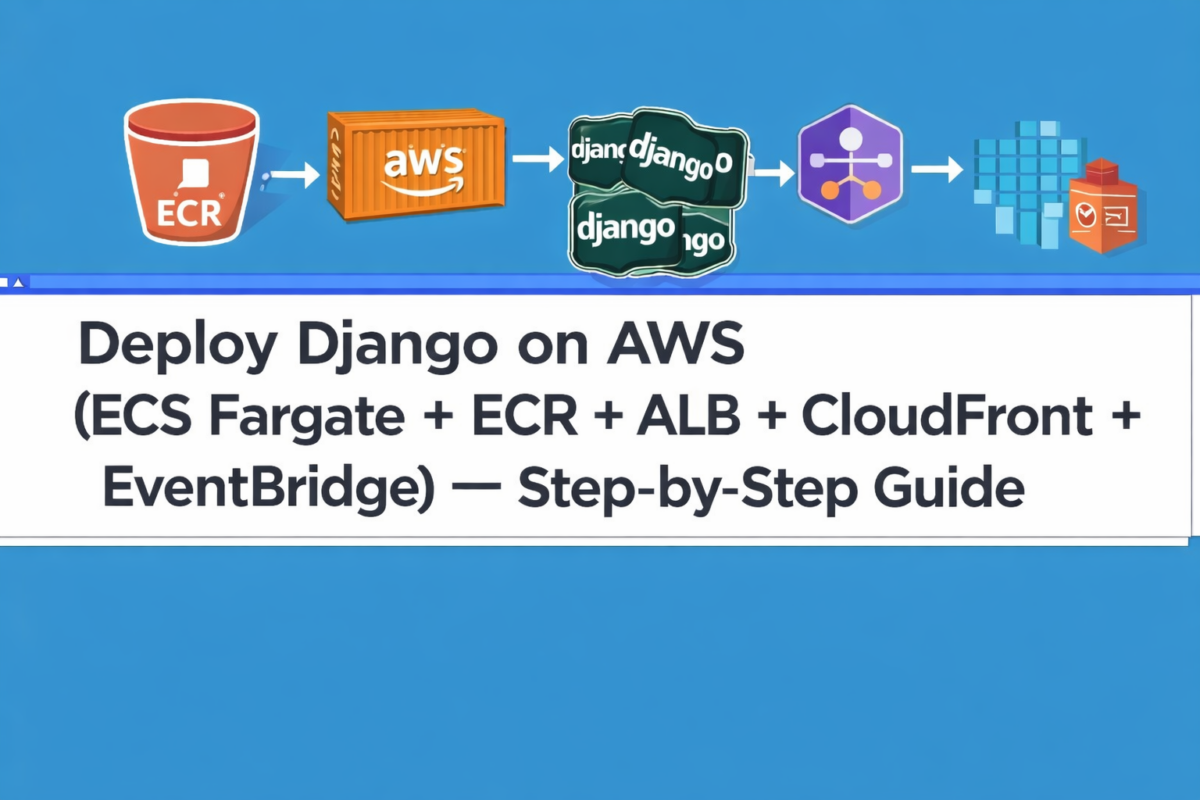
Deploying Django on AWS (ECS Fargate + ECR + ALB + CloudFront + EventBridge) — Step-by-step Guide
This guide documents a production deployment flow for a Django backend running on AWS ECS Fargate, with Docker images stored in ECR, exposed through an Application Load Balancer (ALB), and optionally accelerated/protected by CloudFront.
Scheduled jobs (such as crawlers or daily tasks) can run via EventBridge.
Architecture overview (what’s being used)
- ECR (Elastic Container Registry): stores versioned Docker images (unique tags).
- ECS Fargate: runs your container without managing servers. Your service keeps 1+ tasks alive.
- Task Definition (example-web): the container “blueprint” (image, env vars, ports, CPU/RAM, logs, etc.). Every change creates a new revision (e.g., example-web:3).
- Service (example-backend-service-s2zz1bm3): maintains the desired number of tasks and performs rolling deployments.
- ALB (Application Load Balancer): receives HTTP/HTTPS traffic and routes it to your tasks (Target Group → container:8000).
- CloudFront: can sit in front of the ALB for caching, TLS, WAF, and better latency (you’ll commonly see requests to /admin and /static).
- CloudWatch Logs: container logs (entrypoint, gunicorn, errors, etc.).
- EventBridge (Schedules): runs scheduled workloads (e.g., a daily crawler) by triggering an ECS task.
The 3 key deployment actions
- Build + Push to ECR (unique tag)
- Create a new Task Definition revision that points to that tag
- Update the Service to the new revision + force a new deployment
0) Prerequisites
- Docker running locally
- AWS CLI configured (profile: example)
- Repository with a working Dockerfile + entrypoint.sh
- Permissions for: ECR push, ECS register task definition, ECS update-service
1) Build + Push with a unique tag (ECR)
This step packages your code into a Docker image, tags it uniquely (e.g., short git commit),
and pushes it to ECR.
export AWS_REGION=us-east-2
export AWS_PROFILE=example
export AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=example
export ECR_REPO=example-backend
export ECR_URI=$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com/$ECR_REPO
export IMAGE_TAG=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD)
# Login to ECR
aws ecr get-login-password --region $AWS_REGION --profile $AWS_PROFILE
| docker login --username AWS --password-stdin
$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com
# Build, tag and push
docker build -t $ECR_REPO:$IMAGE_TAG .
docker tag $ECR_REPO:$IMAGE_TAG $ECR_URI:$IMAGE_TAG
docker push $ECR_URI:$IMAGE_TAGExpected result: you should see “Pushed” and a digest: sha256:....
2) Update the Task Definition (example-web) to use that tag
Key idea: even if the image exists in ECR, ECS won’t run it until a Task Definition revision references that exact tag.
Option A (recommended): AWS Console
- Go to ECS → Task definitions → example-web
- Click Create new revision
- In Container: web update the Image URI from:
...:latest
to:030512689265.dkr.ecr.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/example-backend:$IMAGE_TAG - Click Create
✅ Result: you’ll get a new revision, for example example-web:4.
Option B: CLI (advanced equivalent)
This method downloads the current task definition, replaces the image field for the web container,
and registers a new revision.
# Requires jq
export AWS_REGION=us-east-2
export FAMILY=example-web
export NEW_IMAGE="030512689265.dkr.ecr.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/example-backend:$IMAGE_TAG"
# Grab the latest definition and build a registrable JSON
aws ecs describe-task-definition
--task-definition $FAMILY
--region $AWS_REGION
| jq --arg IMG "$NEW_IMAGE" '
.taskDefinition
| del(.taskDefinitionArn,.revision,.status,.requiresAttributes,.compatibilities,.registeredAt,.registeredBy)
| .containerDefinitions |= map(if .name=="web" then .image=$IMG else . end)
' > td.json
# Register the new revision
aws ecs register-task-definition
--cli-input-json file://td.json
--region $AWS_REGION3) Update the Service to the new revision (the actual rollout)
Now you tell the Service to use the new task definition revision and perform a rollout.
Option A (AWS Console)
- ECS → Clusters → example-cluster
- Open the Services tab
- Click example-backend-service-s2zz1bm3
- Click Update
- Under Task definition revision, select the new one (e.g., example
-web:4) - Enable ✅ Force new deployment
- Click Update service
Option B (CLI equivalent)
aws ecs update-service
--cluster example-cluster
--service example-backend-service-s2zz1bm3
--task-definition example-web
--force-new-deployment
--region us-east-24) Confirm it’s deployed (quick checks)
AWS Console
- ECS → Clusters → example-cluster → Services
- Open example-backend-service-s2zz1bm3
- In Deployments verify:
Task definition = example-web:<NEW_REVISION>
and that Running = Desired
CloudWatch Logs
- Look for logs such as:
Collecting static...andxxx static files copied - Ensure there are no entrypoint errors (e.g.,
command not found)
HTTP validation (the real proof)
- /admin loads with proper styling
- /static/… returns 200 (not 404)
- /healthz returns 200 (ALB health checks)
Practical notes
- Avoid latest in production: use unique tags (
git rev-parse --short HEADor a timestamp). - If you pushed an image but nothing changed: most of the time it’s because you didn’t create a new task definition revision that points to that tag.
- Scheduled jobs (EventBridge): run tasks like crawlers without touching the web service (typically ECS “run-task” via schedule).
- CloudFront: great for TLS, WAF, caching, and latency; it commonly uses the ALB as an origin.
 Español
Español