A newly uncovered malvertising campaign is delivering a sophisticated, modular malware framework known as PS1Bot, cybersecurity researchers report.
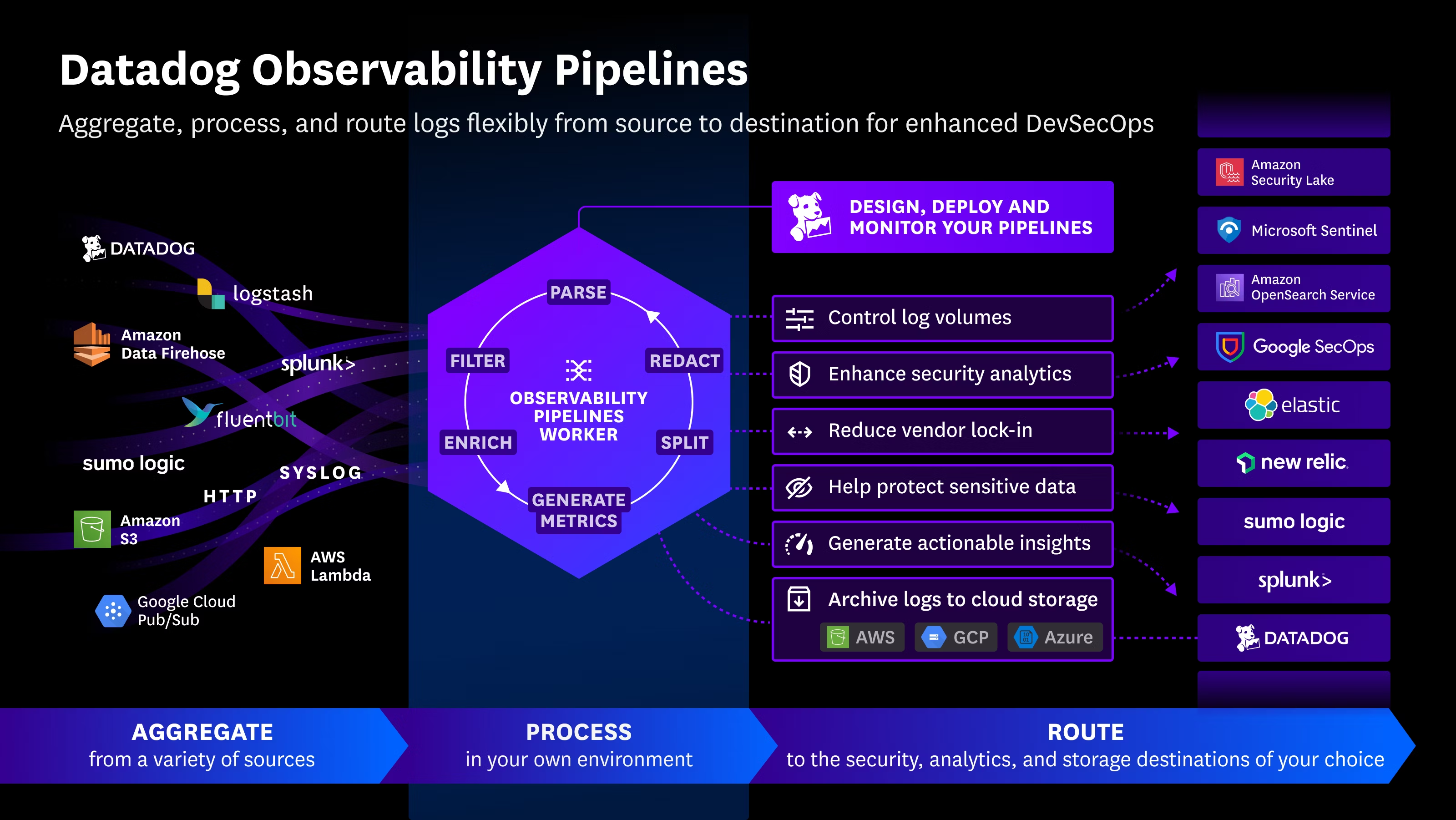
According to Cisco Talos analysts Edmund Brumaghin and Jordyn Dunk, PS1Bot is engineered for stealth and persistence, using in-memory execution techniques to reduce forensic traces. Its modules enable a range of malicious activities, including:
- Data theft from browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and sensitive files
- Keylogging and clipboard monitoring
- System reconnaissance
- Maintaining persistent access to compromised devices
Stealthy, Modular Threat
First detected in early 2025, PS1Bot campaigns utilize malvertising—malicious ads—to distribute PowerShell and C# payloads. The infection chain executes code directly in memory, avoiding disk writes that could trigger antivirus alerts.
Technical similarities link PS1Bot to AHK Bot, an AutoHotkey-based malware previously used by groups such as Asylum Ambuscade and TA866. The campaign also overlaps with earlier ransomware operations deploying Skitnet (a.k.a. Bossnet) to exfiltrate data and gain remote control over infected systems.
Attack Chain
The intrusion begins when a victim downloads a malicious ZIP file delivered via malvertising or SEO poisoning. Inside is a JavaScript file that fetches a scriptlet from a remote server. This scriptlet writes and executes a PowerShell script on the victim’s machine.
The PowerShell script connects to a command-and-control (C2) server, retrieving additional modules to expand PS1Bot’s capabilities. These include:
- Antivirus detection: Identifies security software running on the system
- Screen capture: Sends screenshots to the C2 server
- Wallet grabber: Extracts credentials, wallet seeds, and cryptocurrency data
- Keylogger: Records keystrokes and clipboard activity
- System profiling: Collects detailed host information
- Persistence: Creates a startup PowerShell script to ensure continued C2 communication
Researchers noted that the stealer module uses embedded wordlists to search for password-containing files and wallet seed phrases, which are then exfiltrated.
Rapid Adaptation
The modular structure of PS1Bot allows attackers to quickly roll out new features or updates, making it a versatile and evolving threat.
This discovery comes as Google announced the use of AI-powered large language models (LLMs) to combat invalid traffic (IVT) in advertising. These tools enhance content review and ad placement analysis, leading to a reported 40% drop in IVT from deceptive ad practices.
Source: https://thehackernews.com/2025/08/new-ps1bot-malware-campaign-uses.html
 Español
Español