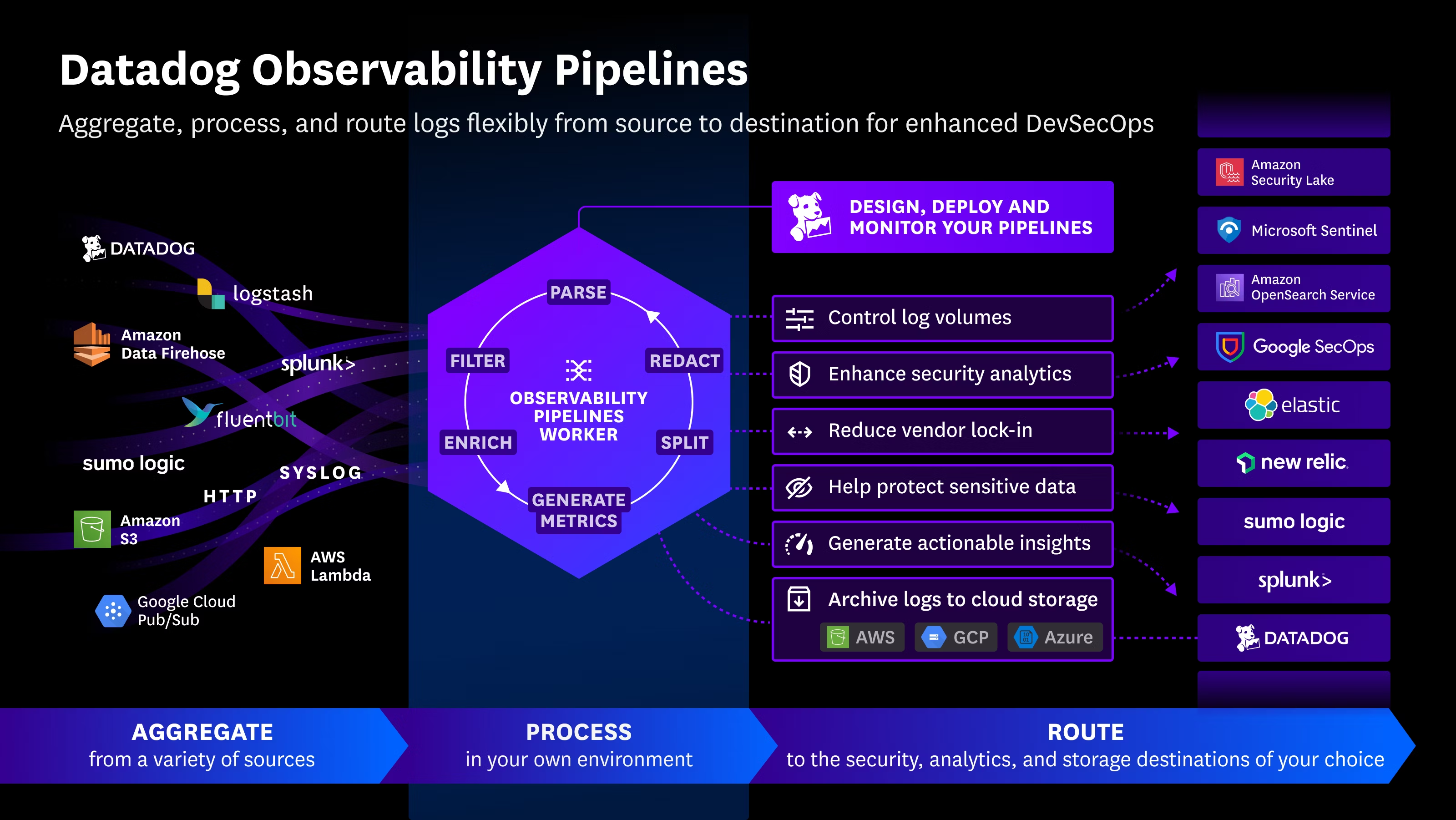
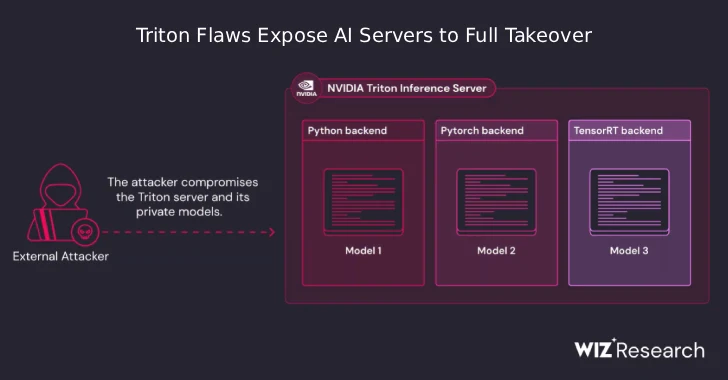
A series of newly identified security flaws in NVIDIA’s open-source Triton Inference Server for Windows and Linux could allow remote attackers to gain full control over vulnerable AI systems—without any authentication.
According to cybersecurity researchers Ronen Shustin and Nir Ohfeld from Wiz, the vulnerabilities—when exploited together—could lead to remote code execution (RCE), effectively handing over server control to threat actors.
Key Vulnerabilities Identified
The security issues affect the Python backend of the Triton server and include:
- CVE-2025-23319 (CVSS 8.1): Enables an attacker to perform an out-of-bounds write by sending a specially crafted request.
- CVE-2025-23320 (CVSS 7.5): Lets an attacker exceed shared memory limits by submitting an excessively large input.
- CVE-2025-23334 (CVSS 5.9): Involves an out-of-bounds read that could leak sensitive memory content.
If exploited, these vulnerabilities could lead to a range of serious consequences, including data leakage, remote code execution, denial of service (DoS), and even data tampering—especially in the case of CVE-2025-23319. NVIDIA has patched all three issues in Triton version 25.07.
Chaining Exploits for Full Server Compromise
Although the flaws are serious on their own, Wiz researchers highlight that chaining them together dramatically increases the risk. An attacker could:
- Abuse CVE-2025-23320 to leak the internal name of the inference server’s shared memory region—a piece of data that should remain confidential.
- Use the leaked key with the other two vulnerabilities to escalate access and completely take over the inference server.
Since the Python backend supports inference requests from popular AI frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, this threat affects a wide range of real-world applications in enterprise AI/ML environments.
Risks for AI-Driven Organizations
These vulnerabilities pose significant dangers, particularly for organizations deploying Triton at scale. A successful exploit could result in:
- Theft of proprietary AI models
- Unauthorized access to sensitive datasets
- Manipulation of AI model outputs
- Establishment of persistence within broader network environments
Wiz’s research underscores the urgency for companies relying on Triton to apply the latest updates immediately and to reevaluate their threat models for AI infrastructure.
Additional Critical Fixes in August
NVIDIA’s August 2025 security bulletin also lists patches for three more critical vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2025-23310
- CVE-2025-23311
- CVE-2025-23317
These flaws could also lead to remote code execution, information disclosure, denial of service, and data tampering if left unpatched.
Although there is no current evidence of these exploits being used in the wild, organizations are strongly urged to apply the 25.07 patch release without delay.
Source: https://thehackernews.com/2025/08/nvidia-triton-bugs-let-unauthenticated.html
 Español
Español